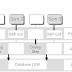
Depending on the configuration of the overall SAP system, SAP can support either a two- or three-tier client/server architecture. The number of tiers depend on how many physical machines are running the software layers; Presentation, (SAP) Application and Database
One tire Architecture
==================
Presentation+Application+Database layer in One system
Layer Description
Presentation Consists of a front end, for users to connect to the SAP system. Typically front end is a tool called SAPGUI or a web browser .
(SAP) Application Runs the typically CPU intensive applications components, such as the SAP DVEBMGS, the Enqueue server , the Message server, and the Dialog processes to name a few.
To increase processing power in a scaled-out approach, several physical servers can be added to the SAP system, each running parts of the Application Layer software components. In the case of Dialog instances, multiple instances can be configured, running with the same SAP SID, but with a different SAP instance numbers.
Database Manages all database transactions. There can only be one database instance for each SAP system.
One tire Architecture
==================
Presentation+Application+Database layer in One system
Layer Description
Presentation Consists of a front end, for users to connect to the SAP system. Typically front end is a tool called SAPGUI or a web browser .
(SAP) Application Runs the typically CPU intensive applications components, such as the SAP DVEBMGS, the Enqueue server , the Message server, and the Dialog processes to name a few.
To increase processing power in a scaled-out approach, several physical servers can be added to the SAP system, each running parts of the Application Layer software components. In the case of Dialog instances, multiple instances can be configured, running with the same SAP SID, but with a different SAP instance numbers.
Database Manages all database transactions. There can only be one database instance for each SAP system.
About Two-Tier Configurations
===========================
A two-tier client server configuration consists of the database (Database Layer = DB ) and all the SAP applications (SAP Application Layer = CI ) running on the same physical machine, as one Serviceguard package (= dbci).
The benefits of a two-tier configuration include:
1. Fewer physical machines to manage and maintain
2. Only one package to create and administer
About Three-Tier Configurations
===========================
A three-tier client server configuration consists of database (Database Layer) on a machine, and some or all of the SAP applications (SAP Application Layer) running on one or more different machines.
Benefits of a Three-Tier Configuration:
1. Making the SAP system more efficient by off-loading CPU intensive SAP processes to one or more machines.
2. Reduce failover times. When a failure occurs, typically, the majority of the downtime is needed to recover the database. Although the total recovery time of a failed database cannot be predicted, failover times can be reduced when the Central Instance and the database are on different machines.
o In the case of a database failure, the Database Serviceguard package will failover to another cluster node, independent of any SAP component.
o In the case of a Central Instance failure, it can be configured to automatically reconnect to a previously failed database, once the database has been restarted by Serviceguard Extension for SAP on Linux on the failover node.
3. When the database and Central Instance are on different machines, a failed Central Instance will not cause a failover of the database.
4. If the CI instance requires even additional off-loading, the Dual Stack Configuration example in the next section shows how the CI can be separated.











No comments:
Post a Comment