=====================================================================
SAP Memory Management
=====================================================================
Virtual memory
All operating systems (supported by SAP) support virtual
memory technology. A process allocates virtual memory using logical (virtual)
addresses. Each process has its own virtual address space. Virtual memory is
fully independent of the physical main memory.
Address space
On 32 bit platforms a virtual address can have values
between 0 and 2^32-1, which restricts the sizes to 4GB. As areas of the virtual
address space are reserved, this leaves about 2GB available on most platforms.
This is not a problem for large SAP systems.
Memory allocation
Allocating memory for a process consists of the following
steps:
1. Reservation of a segment in the physical
memory.
2. Linking the physical memory segment to the
virtual address space of the process, which means reserving a segment of the
same size in the virtual address space and mapping the virtual addresses to
physical addresses.
Local process memory
The operating system differentiates between local process
memory and shared memory. For local process memory the operating system keeps
both allocation steps transparent. Using an API virtual memory only is
requested; the operating system does the other tasks, such as reserving
physical memory, loading and unloading virtual memory into and out of the main
memory.
Shared Memory
If several processes are to access the same memory area,
both allocation steps are not transparent.
One object is created that represents the physical memory
and can be used by various processes. The processes can map the object fully or
partially into the address space. The way this is done varies from platform to
platform. Memory mapped files, unnamed mapped files, and shared memory are
used.
Allocation of memory for the current internal session by
transferring pages out of memory, similarly to operating system paging.
=========================================================================
Functions of the SAP
Memory Management
========================================================================
An application runs in an SAP work process where an ABAP
program is normally executed. The process requires memory to do this, which is
allocated to the process by the memory management system. The order in which
the work process is assigned the memory type depends on the work process type,
either dialog or non-dialog (see SAP Memory Types), and the underlying
operating system.
This is described in more detail in the documentation on the
operating system.
The location of the various memory areas in the virtual
address space is explained in Virtual Address Space of a Work Process.
The area of a user context that is directly accessible is
now extended as needed, if the user context has expanded. For dialog work
processes, the data of the user context, including internal tables is located
in this expanded area.
Whenever a dialog step is executed, a roll action occurs
between the roll buffer in the shared memory and the memory area, which is
allocated according to ztta/roll_first in a dialog process. Then the area in
the shared memory is accessed that belongs to this user context.
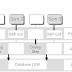
The following graphic displays the roll process performed by
the dispatcher.
● Roll-in cross-user
data is rolled in from the common resource in the work process (and is
processed there).
● Roll-out:
User-specific data is rolled out from the work process in the common resource
(after the dialog step has ended).
=====================================================================
Profile Parameters of
Memory Management
=====================================================================
Memory Management Resources for One Work
Process
ztta/roll_extension: Limit for Extended Memory
ztta/roll_extension_dia: EM Quota for Dialog Work Processes
ztta/roll_extension_nondia: EM Quota for Non-Dialog Work
Processes
abap/heap_area_dia: Heap Memory Limit for Dialog Work
Processes
abap/heap_area_nondia: Heap Memory Limit for Non-Dialog Work
Processes
abap/heap_area_total: Total Quota for Heap Memory
ztta/roll_area: Roll Area
ztta/roll_first: Size of the Initial Allocation from the
Roll Area
Memory Management
Limitations
abap/heap_area_total: Heap Memory Limit
em/initial_size_MB: Extended Memory Pool Size
rdisp/ROLL_SHM: Roll Buffer Size
rdisp/ROLL_MAXFS: Maximum Roll File Size
rdisp/PG_SHM: Size of the Paging Buffer
rdisp/PG_MAXFS: Maximum Size of SAP Paging File
em/blocksize_KB: Segment Size for the Extended Memory
Memory Management
Statistics
em/stat_log_size_MB: Statistics - User Context Size
em/stat_log_timeout: Statistics - User Context Size
Parameters for
controlling the Release of SAP Memory for the Operating System
es/disclaim_threshold_MB
es/disclaim_coasting_time_alloc
es/disclaim_coasting_time_free
es/blockdisclaimsize_KB
es/freelist_compactor
Operating system decides where the extended memory
resides...
When an instance startup a part of memory allocated to
instance called as shared memory.
Which consist of all the buffers, roll area, extended memory
etc.
Whenever the user process any tcode work process alloacate
to user. Data processed by the work process is stored in two memory areas
1. Roll Area: In which user context data is stored like
authorizations, internal table etc.
2. Paging Area : Stores the application program data more
precisely abap command including Extract, Import to memory, Export to memory
call transaction etc.
Paging Area= Page Buffer + Page File
Page buffer is a part of shared memory where as Page File
resides at physical level.
Data swap as per the requirement in Page Buffer and Page
File.
If data processing demands more memory, than the concept of
Heap came into picture which is also called as local memory.
Memory Parameters are there to defines the values for all of
them. If memory utilization for individual work process reached the max. limit
of heap than work process stuck in PRIV mode with all the allocated memory.
For more information visit:-
http://levelx.me/blog/wp-content/uploads/2010/11/SAP-Memory-Management-Collection-by-st4rcH1LD.pdf








Here i had read the content you had posted. It is much interesting so please keep update like this.
ReplyDeleteSAP HR Training in Chennai
SAP SD Training in Chennai
SAP Basis Training in Chennai